
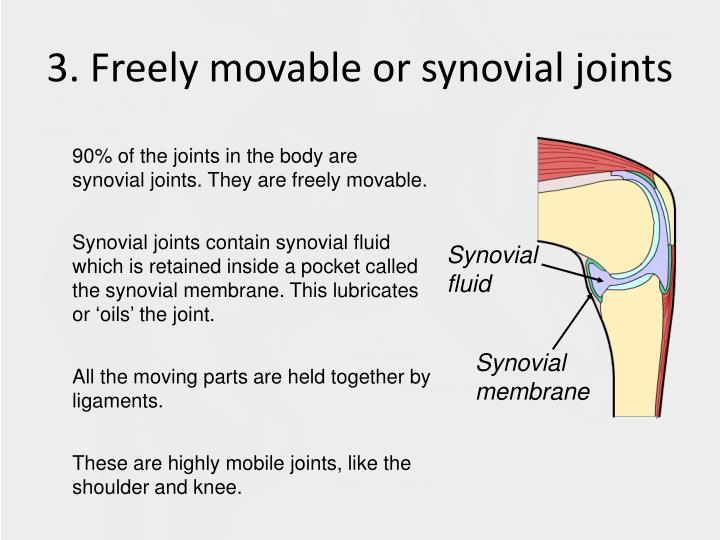
Articular cartilage: the bones of a synovial joint are covered by this layer of hyaline cartilage that lines the epiphyses of joint end of bone with a smooth, slippery surface that does not bind them together articular cartilage functions to absorb shock and reduce friction during movement.Joint capsule: the fibrous capsule, continuous with the periosteum of articulating bones, surrounds the diarthrosis and unites the articulating bones the joint capsule consists of two layers - (1) the outer fibrous membrane that may contain ligaments and (2) the inner synovial membrane that secretes the lubricating, shock absorbing, and joint-nourishing synovial fluid the joint capsule is highly innervated, but without blood and lymph vessels, and receives nutrition from the surrounding blood supply via either diffusion (a slow process) or by convection, a far more efficient process achieved through exercise.Synovial cavity: all diarthroses have the characteristic space between the bones that is filled with synovial fluid.

Synovial joints contain the following structures: As with most other joints, synovial joints achieve movement at the point of contact of the articulating bones. They are the most common and most movable type of joint in the body of a mammal.
The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer of fibrous membrane, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid.
Freely movable joints free#
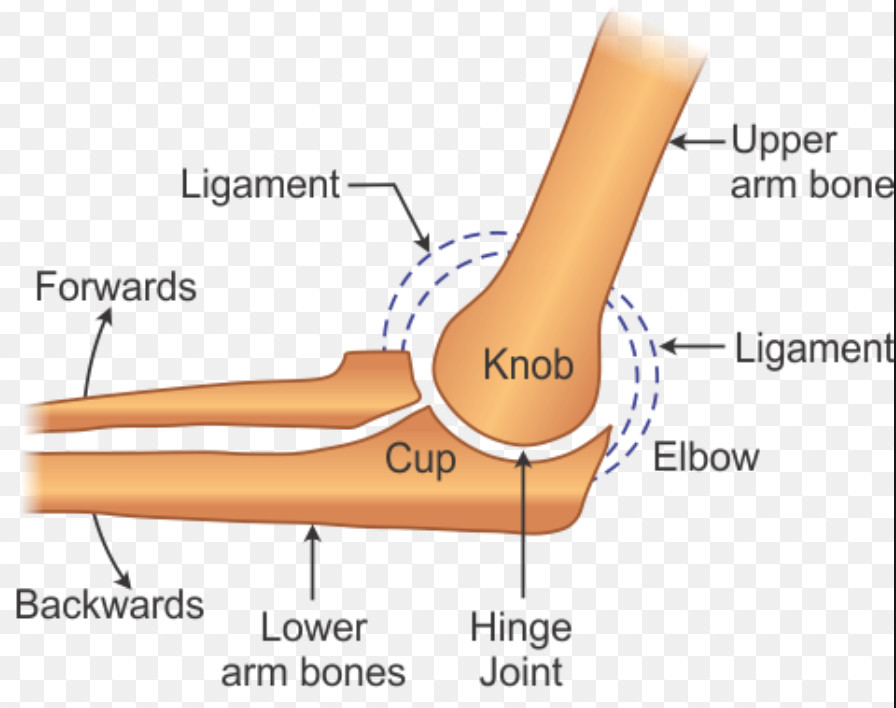
This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
